SCOPE: Saliency-Coverage Oriented Token Pruning for Efficient Multimodal LLMs
Abstract
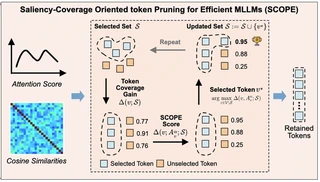
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) typically process a large number of visual tokens, leading to considerable computational overhead, even though many of these tokens are redundant. Existing visual token pruning methods primarily focus on selecting the most salient tokens based on attention scores, which can cause semantic incompleteness. We propose Saliency-Coverage Oriented token Pruning for Efficient MLLMs (SCOPE), which jointly models both the saliency and coverage of the selected visual tokens to better preserve semantic completeness. Specifically, we define set coverage for a given set of selected tokens based on token relationships, then define token-coverage gain for each unselected token to quantify how much additional coverage would be obtained by including it. By integrating saliency into token-coverage gain, we define a SCOPE score and iteratively select the token with the highest SCOPE score. Experiments on multiple vision-language understanding benchmarks with LLaVA-1.5 and LLaVA-Next demonstrate consistent improvements over prior approaches.
Type
Publication
In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) 2025
Authors
Authors
Authors

Authors
Scientist
I am a Scientist at the Centre for Frontier AI Research (CFAR), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore. I also serve as an Adjunct Assistant Professor at the National University of Singapore (NUS).
I received my Ph.D. from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) under the supervision of Prof. Yi Yang.